Protein superfamilies often diverge into subgroups, each adapting the superfamily’s structural core to fill a functional niche. Often a subgroup G diverges further into smaller subgroups, each conserving residues constrained by G’s function, as well as other residues constrained by more specialized functions. Repeated rounds of such divergence have led to hierarchically arranged subgroups, each of which conserves distinctive residues at particular positions. BPPS identifies and characterizes these subgroups by partitioning a multiple sequence alignment (MSA) into a hierarchically nested series of sub-MSAs based on correlated residue patterns that are distinctive of each subgroup.
Tarball containing the latest BPPS executable. For original source code see SIPRIS webpage.
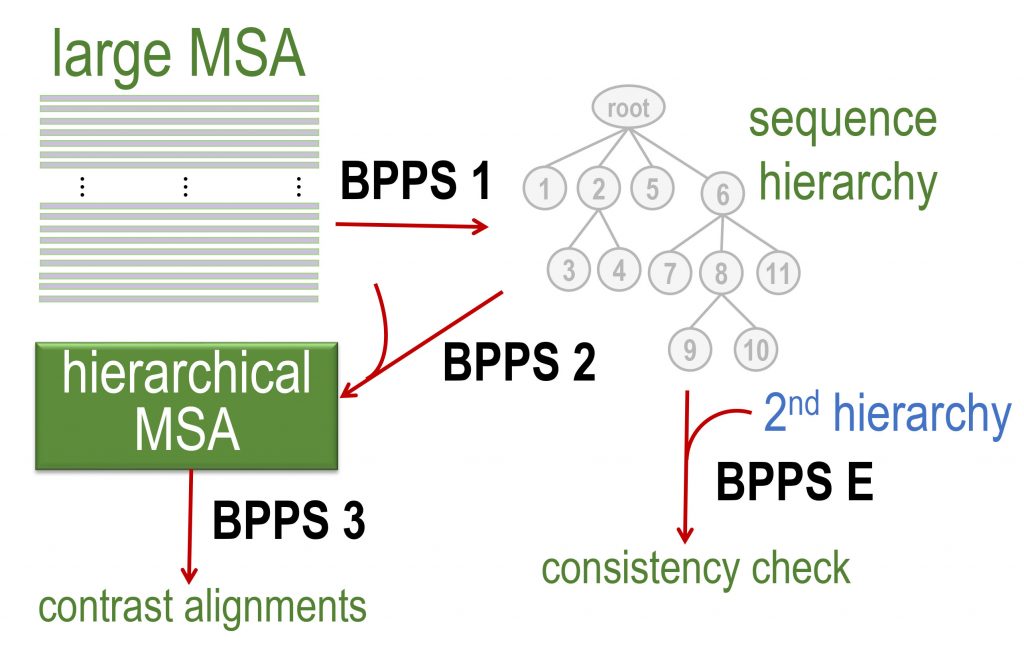
Overview of the steps performed by the BPPS program:
REFERENCES:
Neuwald, A.F., L. Aravind & S.F. Altschul. Inferring Joint Sequence-Structural Determinants of Protein Functional Specificity. eLife 2018. doi:10.7554/eLife.29880.001. https://elifesciences.org/articles/29880
Neuwald, A.F and S. F. Altschul. 2016. Inference of Functionally-Relevant N-Acetyltransferase Residues Based on Statistical Correlations. Plos Comp. Biol. 12(12):e1005294.
Neuwald, A.F. 2014. A Bayesian sampler for optimization of protein domain hierarchies. Journal of Computational Biology 21(3):269-286. PMID: 24559108.
Neuwald, A.F. 2014. Protein Domain Hierarchy Gibbs Sampling Strategies. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology 13(4):497-517.
Neuwald, A.F. 2011. Surveying the manifold divergence of an entire protein class for statistical clues to underlying biochemical mechanisms. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology 10(1): Article 36.
Neuwald A.F., Kannan N., Poleksic A., Hata N., and Liu J.S. 2003. Ran’s C-terminal, basic patch and nucleotide exchange mechanisms in light of a canonical structure for Rab, Rho, Ras and Ran GTPases. Genome Research 13(4): 673-692.
FUNDING: The National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences grants R01GM078541 and R01GM125878.
BPPS E: Executes a routine (evalBPPS) to evaluate the consistency between two different BPPS-generated hierarchies based on the same input MSA. Comparisons among multiple hierarchies in this way provides a measure of consistency.
Reference: Neuwald, A.F. 2014. Evaluating, comparing and interpreting protein domain hierarchies. Journal of Computational Biology 21(4): 287-302

CHAIN: Contrast Hierarchical Alignment & Interaction Network Analysis (early predecessor of BPPS)
REFERENCE: Neuwald A.F., Kannan N., Poleksic A., Hata N., and Liu J.S. 2003. Ran’s C-terminal, basic patch and nucleotide exchange mechanisms in light of a canonical structure for Rab, Rho, Ras and Ran GTPases. Genome Research 13(4): 673-692.